CONTENIDOS DESTACADOS
Un plug-in del drone Crazyflie para el simulador ARGoS

Presentamos nuestro nuevo plug-in para el simulador ARGoS que implementa el drone Crazyflie. Éste incluye sus controladores, sensores y algunas de sus placas de expansión. Nuestro desarrollo se basa en el antiguo drone Spiri, al cuál se le ha actualizado el controlador por posición, añadido un nuevo controlador por velocidad, anillo de LEDs, camera onboard, y un modelo de descarga de batería.
Un plug-in del robot E-Puck2 para el simulador ARGoS
Presentamos un nuevo plug-in para el simulador ARGoS que implementa el modelo del robot E-Puck2, incluyendo su representación gráfica, sensores y actuadores. Nuestro desarrollo se basa en el modelo del antiguo robot E-Puck (versión 1) al cual hemos actualizado los sensores existentes (proximidad, iluminación, suelo, cámara, y batería) y también añadido otros nuevos (tiempo de vuelo y codificadores simulados) implementados desde cero.
Algoritmo Generador de Flujos
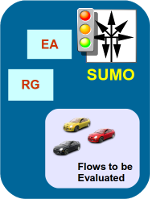
Presentamos un nuevo enfoque para calcular flujos vehiculares realistas para los simuladores de tráfico, llamado Flow Generator Algorithm (FGA). Partimos de un mapa original importado desde OpenStreetMap y datos de tráfico obtenidos por diferentes puntos de medición, publicados por las autoridades de la ciudad para producir un modelo que consiste en un mapa de simulación y una serie de flujos de tráfico (rutas + vehículos) los cuales coinciden con los valores reales.
Yellow Swarm

El tráfico congestionado es una de las principales preocupaciones de los ciudadanos de las grandes ciudades. En este artículo proponemos un nuevo sistema, llamado Yellow Swarm, con el propósito de mejorar el tráfico rodado utilizando una solución de bajo coste y fácil implementación, la cual se apoya en un conjunto de paneles LED, ubicados en diferentes puntos de la ciudad, con el objetivo de distribuir los vehículos por sus calles.
Green Swarm

Se propone una nueva arquitectura de movilidad llamada Green Swarm para reducir las emisiones de gases de efecto invernadero del tráfico rodado en ciudades inteligentes. Se optimizan los flujos vehiculares en cuatro ciudades Europeas: Málaga, Estocolmo, Berlín y Paris. Se crean nuevos casos de estudio importando el trazado urbano real junto con los semáforos desde OpenStreetMap en el simulador de tráfico SUMO para encontrar las mejores rutas y comunicarlas a los conductores.
Red Swarm
Las ciudades hoy día evolucionan rápidamente. Un gran número de personas residen o están contemplando la posibilidad de trasladar su domicilio habitual a una ciudad, aumentando así la demanda de servicios, lo que supone una nueva fuente de problemas complejos. Smart Cities es una iniciativa mundial encaminada a mejorar la explotación de recursos en la ciudad de forma que se ofrezcan servicios de mejor calidad a sus habitantes.
El Algoritmo epiGenético
El Algoritmo epiGenético (epiGA) es una nueva propuesta que consiste en un conjunto de estrategias, basadas en la computación evolutiva, inspiradas en la naturaleza, en especial en la epigenética, con el fin de resolver problemas combinatorios complejos. Nos interesa como las histonas y el ADN se colapsan para formar nucleosomas, como esto afecta la replicación génica durante la reproducción, y como los mecanismos epigenéticos modifican la expresión génica a través de la metilación. Código fuente en GitLab: JAVA y Python.
Proyecto CoMVeT

Emotiv EPOC es un casco que permite registrar a alta resolución la actividad cerebral, procesarla y enviarla a un PC de forma inalámbrica. Mediante la correcta interpretación de estas señales, este casco representa un nuevo tipo de interfaz hombre-máquina (HCI). El casco posee una serie de sensores (humedecidos con una solución salina) para detectar los pensamientos básicos del usuario, así como sus sentimientos y emociones, incluyendo las que van acompañadas de gestos expresivos.
Proyecto VIGIA

El proyecto VIGIA es un desarrollo realizado en el marco de la asignatura Ingeniería del Software: Proyectos. En el mismo se aborda la construcción de un sistema de vigilancia que permite controlar una cámara de forma remota mediante los movimientos de la cabeza del usuario utilizando el mando de la consola Wii, el Wiimote, para simular una ventana virtual.
CONTENIDO MULTIMEDIA
PROYECTOS DE INVESTIGACIÓN

El proyecto COMBO (Optimal integration of connected and automated shuttles with passenger and freight transport systems) tiene como objetivo el estudio de las implicaciones, beneficios e impactos a medio y largo plazo producto de la integración de mini buses conectados y autónomos con los sistemas de transporte existentes. El proyecto busca producir un sistema de toma de decisiones para facilitar esta integración. Leer más...
El proyecto ADARS (Automating the Design of Autonomous Robot Swarms) busca proponer una única solución al diseño de sistemas autónomos distribuidos respondiendo la siguiente pregunta: Es posible generar automáticamente comportamientos eficientes y reutilizables para sistemas distribuidos espaciales y aeroespaciales (DASS)? Con este fin, ADARS realizará avances del estado-del-arte en el campo de enjambre de robots y diseño automático de algoritmos. Leer más...
El proyecto HUNTED (Heterogeneous multi-swarms of UNmanned auTonomous systEms for mission Deployment) tiene como objetivo el diseño de una nueva generación de modelos de movilidad para enjambres heterogéneos múltiples, compuestos por sistemas autónomos no tripulados (UAS - Unmanned Autonomous Systems), orientados a tareas de vigilancia y seguimiento de amenazas inminentes. Estos enjambres están compuestos por varios vehículos moviéndose de forma autónoma y coordinada por el aire, tierra o mar. Leer más...

En el proyecto 6CITY (TIN2017-88213-R) se presenta la hipótesis de trabajo de poder resolver muchos de los problemas de las ciudades inteligentes (según la UE: economía, movilidad, gobierno, ciudadanos, calidad de vida, medio ambiente) los cuales son de naturaleza multidisciplinaria, aparentemente independientes, y que requieren un vasta experiencia científica para afrontarlos. Dentro de la propuesta se encuentran los algoritmos avanzados para búsqueda y optimización que puedan aprender por sí mismos en las situaciones en que el conocimiento previo del problema es muy limitado. Leer más...

El proyecto MOVEON (TIN2014-57341-R) consiste en una ambiciosa propuesta de investigación centrada en los retos relacionados con trasporte inteligente y movilidad inteligente. Nuestro enfoque se realiza desde la perspectiva de construcción de nuevas aplicaciones basadas en motores de resolución basados en metaheurísticas reforzados con metodologías y teorías que forman parte de la contribución realizada por nuestro equipo para conseguir "inteligencia holística". Leer más...

El proyecto MAXCT (OTRI # 8.06/5.47.4356 - AOP GGI3003IDI) comprende a dos aplicaciones que se ejecutan para mejorar el flujo del tráfico en una ciudad: El sistema HITUL (Holistic Intelligente for Traffic Urban Lights) orientado a la optimización de los semáforos existentes y el sistema CTPATH mediante la cual los conductores pueden recibir información respecto a sus rutas basada en sus preferencias. Leer más...
El proyecto roadME (TIN2011-28194) tiene el propósito de caracterizar, diseñar y evaluar técnicas metaheurísticas que sean capaces de resolver problemas del mundo real, en particular, aplicaciones de redes de comunicaciones vehiculares (VANET). Nuestra hipótesis es que las metaheurísticas estándares no sin capaces por si solas de resolver los requisitos de muchos de los problemas complejos como este, ya que nos enfrentamos a tiempos de ejecución de unos pocos segundos, requisitos específicos de cada usuario, problemas escalables a dimensiones muy grandes y la necesidad de robustez en diferentes escenarios de trabajo. Leer más...

El proyecto PATIO: Técnicas de aprendizaje colaborativo y modelado de usuario aplicadas a la integración multicultural (TIC-4273), ha sido desarrollado por el grupo de Investigación y Aplicaciones en Inteligencia Artificial perteneciente al Departamento de Lenguajes y Ciencias de la Computación de la Universidad de Málaga, subvencionado en la convocatoria de proyectos de excelencia de la Consejería de Innovación, Ciencia y Empresa (convocatoria 2008) de la Junta de Andalucía. Leer más...
PUBLICACIONES EN REVISTAS CIENTÍFICAS
Listado Completo
Optimising Last-Mile Parcel Delivery Using Connected Autonomous Shuttles
Daniel H. Stolfi and Cindy Guerlain and Sébastien Faye. Optimising Last-Mile Parcel Delivery Using Connected Autonomous Shuttles. In: IEEE Access, pp. 1-1, 2025.
doi> 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3637526 | [BibTex]@Article{Stolfi2025b,
author = {Stolfi, Daniel H. and Guerlain, Cindy and Faye, S\'{e}bastien},
journal = {IEEE Access},
title = {Optimising Last-Mile Parcel Delivery Using Connected Autonomous Shuttles},
year = {2025},
pages = {1-1},
doi = {10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3637526},
keywords = {Logistics;Postal services;Proposals;Genetic algorithms;Urban areas;Space shuttles;Heuristic algorithms;Costs;Routing;Silicon;parcel delivery;autonomous shuttles;last-mile delivery;parcel locker;city logistics;genetic algorithm},
}

Connectivity-Aware Route Design and Frequency Setting for Connected and Automated Shuttles
Elhadja Chaalal and Daniel H. Stolfi and Ayat Zaki-Hindi and Sébastien Faye. Connectivity-Aware Route Design and Frequency Setting for Connected and Automated Shuttles. In: IEEE Access, vol. 13, pp. 173939-173951, 2025.
doi> 10.1109/access.2025.3615310 | [BibTex]@Article{Chaalal2025,
author = {Chaalal, Elhadja and Stolfi, Daniel H. and Zaki-Hindi, Ayat and Faye, S\'{e}bastien},
journal = {IEEE Access},
title = {Connectivity-Aware Route Design and Frequency Setting for Connected and Automated Shuttles},
year = {2025},
issn = {2169-3536},
pages = {173939--173951},
volume = {13},
doi = {10.1109/access.2025.3615310},
publisher = {Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)},
}

Escorting drone swarm formation: a swarm intelligence and evolutionary optimisation approach
Daniel H. Stolfi and Grégoire Danoy. Escorting drone swarm formation: a swarm intelligence and evolutionary optimisation approach. In: Swarm Intelligence, vol. 19, No. 3, pp. 245-272, 2025.
doi> 10.1007/s11721-025-00250-5 | [BibTex]@Article{Stolfi2025,
author = {Stolfi, Daniel H. and Danoy, Gr\'{e}goire},
journal = {Swarm Intelligence},
title = {Escorting drone swarm formation: a swarm intelligence and evolutionary optimisation approach},
year = {2025},
issn = {1935-3820},
month = jun,
number = {3},
pages = {245--272},
volume = {19},
doi = {10.1007/s11721-025-00250-5},
groups = {My Publications},
publisher = {Springer Science and Business Media LLC},
}

Evolutionary swarm formation: From simulations to real world robots
Daniel H. Stolfi and Grégoire Danoy. Evolutionary swarm formation: From simulations to real world robots. In: Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, vol. 128, pp. 107501, 2024.
doi> 10.1016/j.engappai.2023.107501 | [BibTex]@Article{Stolfi2024,
author = {Daniel H. Stolfi and Gr\'{e}goire Danoy},
journal = {Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence},
title = {Evolutionary swarm formation: From simulations to real world robots},
year = {2024},
issn = {0952-1976},
pages = {107501},
volume = {128},
doi = {10.1016/j.engappai.2023.107501},
groups = {My Publications},
keywords = {Swarm robotics, Evolutionary algorithm, E-Puck2, ARGoS simulator, Robot formation},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0952197623016858},
}

Optimising Robot Swarm Formations by Using Surrogate Models and Simulations
Daniel H. Stolfi and Grégoire Danoy. Optimising Robot Swarm Formations by Using Surrogate Models and Simulations. In: Applied Sciences, vol. 13, No. 10, 2023.
doi> 10.3390/app13105989 | [BibTex] | [Archivos]@Article{Stolfi2023a,
author = {Stolfi, Daniel H. and Danoy, Gr\'{e}goire},
journal = {Applied Sciences},
title = {Optimising Robot Swarm Formations by Using Surrogate Models and Simulations},
year = {2023},
issn = {2076-3417},
number = {10},
volume = {13},
article-number = {5989},
doi = {10.3390/app13105989},
url = {https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/13/10/5989},
}

Design and analysis of an E-Puck2 robot plug-in for the ARGoS simulator
Daniel H. Stolfi and Grégoire Danoy. Design and analysis of an E-Puck2 robot plug-in for the ARGoS simulator. In: Robotics and Autonomous Systems, vol. 164, pp. 104412, 2023.
doi> 10.1016/j.robot.2023.104412 | [BibTex] | [Archivos]@Article{Stolfi2023,
author = {Daniel H. Stolfi and Gr\'{e}goire Danoy},
journal = {Robotics and Autonomous Systems},
title = {Design and analysis of an {E-Puck2} robot plug-in for the {ARGoS} simulator},
year = {2023},
issn = {0921-8890},
pages = {104412},
volume = {164},
doi = {10.1016/j.robot.2023.104412},
keywords = {E-puck2, ARGoS, Computer simulations, Sensors, Swarm robotic},
url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921889023000519},
}

An Evolutionary Algorithm to Optimise a Distributed UAV Swarm Formation System
Daniel H. Stolfi and Grégoire Danoy. An Evolutionary Algorithm to Optimise a Distributed UAV Swarm Formation System. In: Applied Sciences, vol. 12, No. 20, 2022.
doi> 10.3390/app122010218 | [BibTex]@Article{Stolfi2022b,
author = {Stolfi, Daniel H. and Danoy, Gr\'{e}goire},
journal = {Applied Sciences},
title = {An Evolutionary Algorithm to Optimise a Distributed UAV Swarm Formation System},
year = {2022},
issn = {2076-3417},
number = {20},
volume = {12},
article-number = {10218},
doi = {10.3390/app122010218},
url = {https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/12/20/10218},
}

SuSy-EnGaD: Surveillance System Enhanced by Games of Drones
Daniel H. Stolfi and Matthias R. Brust and Grégoire Danoy and Pascal Bouvry. SuSy-EnGaD: Surveillance System Enhanced by Games of Drones. In: Drones, vol. 6, No. 1, 2022.
doi> 10.3390/drones6010013 | [BibTex] | [Archivos]@Article{drones6010013,
AUTHOR = {Stolfi, Daniel H. and Brust, Matthias R. and Danoy, Gr\'{e}goire and Bouvry, Pascal},
TITLE = {{SuSy-EnGaD}: Surveillance System Enhanced by Games of Drones},
JOURNAL = {Drones},
VOLUME = {6},
YEAR = {2022},
NUMBER = {1},
ARTICLE-NUMBER = {13},
URL = {https://www.mdpi.com/2504-446X/6/1/13},
ISSN = {2504-446X},
DOI = {10.3390/drones6010013},
FILE = {https://gitlab.uni.lu/hunted/susy-engad-surveillance-system-enhanced-by-games-of-drones}
}

A competitive Predator–Prey approach to enhance surveillance by UAV swarms
Daniel H. Stolfi and Matthias R. Brust and Grégoire Danoy and Pascal Bouvry. A competitive Predator–Prey approach to enhance surveillance by UAV swarms. In: Applied Soft Computing, vol. 111, pp. 107701, 2021.
doi> 10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107701 | [BibTex] | [Archivos]@article{Stolfi2021c,
title = {A competitive Predator–Prey approach to enhance surveillance by UAV swarms},
journal = {Applied Soft Computing},
volume = {111},
pages = {107701},
year = {2021},
issn = {1568-4946},
doi = {10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107701},
author = {Daniel H. Stolfi and Matthias R. Brust and Gr\'{e}goire Danoy and Pascal Bouvry},
keywords = {Swarm robotics, Computer simulation, Mobility model, Unmanned aerial vehicle, Competitive coevolutionary genetic algorithm},
}

Yellow Swarm: LED panels to advise optimal alternative tours to drivers in the city of Malaga
Daniel H. Stolfi and Enrique Alba. Yellow Swarm: LED panels to advise optimal alternative tours to drivers in the city of Malaga. In: Applied Soft Computing, vol. 109, pp. 107566, 2021.
doi> 10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107566 | [BibTex]@Article{Stolfi2021b,
author = {Daniel H. Stolfi and Enrique Alba},
journal = {Applied Soft Computing},
title = {Yellow Swarm: LED panels to advise optimal alternative tours to drivers in the city of Malaga},
year = {2021},
issn = {1568-4946},
pages = {107566},
volume = {109},
doi = {10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107566},
groups = {My Publications},
keywords = {epiGenetic algorithm, Smart mobility, LED panel, Travel time, Greenhouse gas emissions, Fuel consumption}
}

CONSOLE: intruder detection using a UAV swarm and security rings
Daniel H. Stolfi and Matthias R. Brust and Grégoire Danoy and Pascal Bouvry. CONSOLE: intruder detection using a UAV swarm and security rings. In: Swarm Intelligence, vol. 15, No. 3, pp. 205-235, 2021.
doi> 10.1007/s11721-021-00193-7 | [BibTex]@Article{Stolfi2021a,
author = {Daniel H. Stolfi and Matthias R. Brust and Gr{\'{e}}goire Danoy and Pascal Bouvry},
journal = {Swarm Intelligence},
title = {CONSOLE: intruder detection using a UAV swarm and security rings},
year = {2021},
issn = {1935-3820},
number = {3},
pages = {205--235},
volume = {15},
doi = {10.1007/s11721-021-00193-7},
groups = {My Publications},
publisher = {Springer Science and Business Media {LLC}},
refid = {Stolfi2021},
url = {10.1007/s11721-021-00193-7},
}

Swarm-based counter UAV defense system
Matthias R. Brust and Grégoire Danoy and Daniel H. Stolfi and Pascal Bouvry. Swarm-based counter UAV defense system. In: Discover Internet of Things, vol. 1, No. 1, 2021.
doi> 10.1007/s43926-021-00002-x | [BibTex]@Article{Brust2021,
author = {Matthias R. Brust and Gr{\'{e}}goire Danoy and Daniel H. Stolfi and Pascal Bouvry},
journal = {Discover Internet of Things},
title = {Swarm-based counter {UAV} defense system},
year = {2021},
month = {feb},
number = {1},
volume = {1},
doi = {10.1007/s43926-021-00002-x},
groups = {My Publications},
publisher = {Springer Science and Business Media {LLC}},
}

UAV-UGV-UMV Multi-Swarms for Cooperative Surveillance
Daniel H. Stolfi and Matthias R. Brust and Grégoire Danoy and Pascal Bouvry. UAV-UGV-UMV Multi-Swarms for Cooperative Surveillance. In: Frontiers in Robotics and AI, vol. 8, 2021.
doi> 10.3389/frobt.2021.616950 | [BibTex]@article{Stolfi2021,
author = {Stolfi, Daniel H. and Brust, Matthias R. and Danoy, Gr{\'{e}}goire and Bouvry, Pascal},
doi = {10.3389/frobt.2021.616950},
issn = {2296-9144},
journal = {Frontiers in Robotics and AI},
month = {feb},
title = {{UAV-UGV-UMV Multi-Swarms for Cooperative Surveillance}},
url = {https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frobt.2021.616950/full},
volume = {8},
year = {2021}
}

Emerging Inter-Swarm Collaboration for Surveillance Using Pheromones and Evolutionary Techniques
Daniel H. Stolfi and Matthias R. Brust and Grégoire Danoy and Pascal Bouvry. Emerging Inter-Swarm Collaboration for Surveillance Using Pheromones and Evolutionary Techniques. In: Sensors, vol. 20, No. 9, 2020.
doi> 10.3390/s20092566 | [BibTex]@article{s20092566,
author = {Stolfi, Daniel H. and Brust, Matthias R. and Danoy, Gr{\'e}goire and Bouvry, Pascal},
title = {Emerging Inter-Swarm Collaboration for Surveillance Using Pheromones and Evolutionary Techniques},
journal = {Sensors},
volume = {20},
year = {2020},
number = {9},
url = {https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/20/9/2566},
issn = {1424-8220},
doi = {10.3390/s20092566}
}

Can I Park in the City Center? Predicting Car Park Occupancy Rates in Smart Cities
Daniel H. Stolfi and Enrique Alba and Xin Yao. Can I Park in the City Center? Predicting Car Park Occupancy Rates in Smart Cities. In: Journal of Urban Technology, vol. 27, No. 4, pp. 27-41, 2020.
doi> 10.1080/10630732.2019.1586223 | [BibTex] | [Archivos]@article{doi:10.1080/10630732.2019.1586223,
author = {Stolfi, Daniel H. and Alba, Enrique and Yao, Xin},
title = {Can I Park in the City Center? Predicting Car Park Occupancy Rates in Smart Cities},
journal = {Journal of Urban Technology},
volume = {27},
number = {4},
pages = {27-41},
year = {2020},
publisher = {Routledge},
doi = {10.1080/10630732.2019.1586223},
}

Green Swarm: Greener routes with bio-inspired techniques
Daniel H. Stolfi and Enrique Alba. Green Swarm: Greener routes with bio-inspired techniques. In: Applied Soft Computing, vol. 71, pp. 952-963, 2018.
doi> 10.1016/j.asoc.2018.07.032 | [BibTex] | [Archivos]@article{STOLFI2018952,
title = "Green Swarm: Greener routes with bio-inspired techniques",
journal = "Applied Soft Computing",
volume = "71",
pages = "952 - 963",
year = "2018",
issn = "1568-4946",
doi = "10.1016/j.asoc.2018.07.032",
url = "http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1568494618304204",
author = "Daniel H. Stolfi and Enrique Alba",
keywords = "Evolutionary algorithm, Road traffic, Smart city, Smart mobility, Gas emissions, Wi-Fi connections",
}

Generating realistic urban traffic flows with evolutionary techniques
Daniel H. Stolfi and Enrique Alba. Generating realistic urban traffic flows with evolutionary techniques. In: Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, vol. 75, pp. 36-47, 2018.
doi> 10.1016/j.engappai.2018.07.009 | [BibTex] | [Archivos]@article{STOLFI201836,
title = "Generating realistic urban traffic flows with evolutionary techniques",
journal = "Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence",
volume = "75",
pages = "36 - 47",
year = "2018",
issn = "0952-1976",
doi = "10.1016/j.engappai.2018.07.009",
url = "http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0952197618301532",
author = "Daniel H. Stolfi and Enrique Alba",
keywords = "Evolutionary algorithm, Traffic simulation, Smart mobility, SUMO, Road traffic optimization, O–D matrix",
}

Epigenetic algorithms: A New way of building GAs based on epigenetics
Daniel H. Stolfi and Enrique Alba. Epigenetic algorithms: A New way of building GAs based on epigenetics. In: Information Sciences, vol. 424, No. Supplement C, pp. 250-272, 2018.
doi> 10.1016/j.ins.2017.10.005 | [BibTex] | [Archivos1] | [Archivos2]@article{STOLFI2018250,
author = {Stolfi, Daniel H. and Alba, Enrique},
doi = {10.1016/j.ins.2017.10.005},
issn = {0020-0255},
journal = {Information Sciences},
keywords = {Evolutionary algorithm; Epigenetics; MKP; Bio-insp},
number = {Supplement C},
pages = {250--272},
title = {{Epigenetic algorithms: A New way of building GAs based on epigenetics}},
url = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020025517309921},
volume = {424},
year = {2018},
}

Red Swarm: Reducing travel times in smart cities by using bio-inspired algorithms
Daniel H. Stolfi and Enrique Alba. Red Swarm: Reducing travel times in smart cities by using bio-inspired algorithms. In: Applied Soft Computing, vol. 24, pp. 181-195, 2014.
doi> 10.1016/j.asoc.2014.07.014 | [BibTex]@article{Stolfi2014,
title = "Red Swarm: Reducing travel times in smart cities by using bio-inspired algorithms",
journal = "Applied Soft Computing",
volume = "24",
pages = "181 - 195",
year = "2014",
issn = "1568-4946",
doi = "10.1016/j.asoc.2014.07.014",
author = "Daniel H. Stolfi and Enrique Alba",
keywords = "Evolutionary algorithm, Road traffic, Smart city, Smart mobility, WiFi connections, Traffic light"
}